Systematic Review: CBD Dosing Across Conditions (2023)
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology
A comprehensive review in Journal of Clinical Medicine Research evaluated CBD doses ranging from <1 to 50 mg/kg/day, covering epilepsy, anxiety, pain, and sleep disorders. It concluded that most effective therapeutic doses fall between 300–600 mg/day, while wellness use may still be beneficial at lower exposures.
Translational Investigation of the Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol (CBD): Toward a New Age (2018)
Frontiers in Immunology
This review highlights CBD's potential as an anxiolytic and antipsychotic agent, suggesting its use in various psychiatric disorders.
Scope & Purpose
Examines how various cannabis compounds (phytocannabinoids, terpenes, etc.) exert anti-inflammatory effects. Looks at molecular mechanisms, relevant receptors, cytokines, signaling pathways, and combination/synergy effects.
Receptors & Pathways Involved
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a major modulator. Compounds act via CB1 and CB2 receptors. Other targets include: transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, G protein-coupled receptors (GPRs), adenosine receptors, toll-like receptors (TLRs), nuclear receptors (like PPAR), etc. Key pro-inflammatory cytokines reduced include TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, etc. Processes like oxidative stress, COX-2, iNOS expression, NF-κB activation are discussed.
Preclinical & Clinical Anti-Inflammatory Review (2022)
Frontiers in Pharmacology
A broad review summarized CBD’s immunomodulatory effects, confirming it lowers pro-inflammatory cytokines both in vitro and in vivo. Evidence includes reductions in skin inflammatory mediators and intestinal inflammation—supporting CBD's potential role in treating inflammatory disorders.
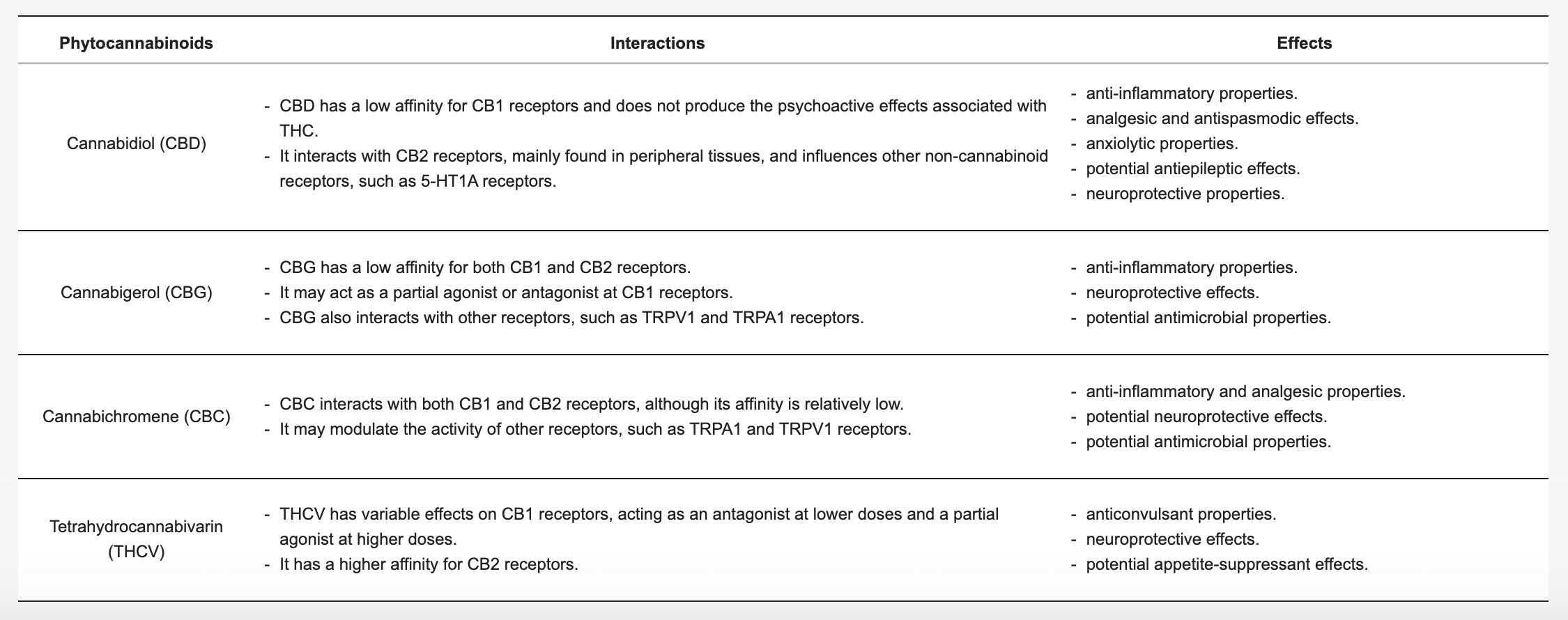
Phytocannabinoids: Exploring Pharmacological Profiles and Their Impact on Therapeutical Use (2024)
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects: A study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences discusses the pharmacological profiles of cannabinoids, including CBC, highlighting its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Research indicates that CBG binds to various targets in the endocannabinoid system, exhibiting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which may be beneficial in neuroinflammatory disorders.
Table excerpt from article: